解決網頁中文字型的缺字問題
2019-10-30

最近有個項目需要在網頁使用一些手寫風格的中文字型,眾所周知這些字型的缺字問題是非常嚴重的,在正常情況下系統會自動補字,但我發現在網頁上很多缺字都會直接變成空白,以下就來看看我解決的方法
找出沒有補字的原因
如果沒興趣可以跳過這個部份
下載並找出 Setofont 的缺字
首先下載瀨戶字體 Seto font,取得一個 .ttf 檔,這裡我把它命名為 setofont.ttf,然後建立一個簡單的 html 網頁測試字體
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
@font-face {
font-family: setofont;
src: url(setofont.ttf);
}
strong {
font-family: setofont, "微軟正黑體", "華文黑體", serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>白川鄉旅行</p>
<p><strong>白川鄉旅行</strong></p>
</body>
</html>在網頁打開 html 可以看到 setofont 的「鄉」字變成空白了,就算是使用了 Windows 的「微軟正黑體」和 MacOS 的「華文黑體」作為 fallback 也沒辦法成功補字

用 FontForge 找出問題所在
為了找出問題所在,我們需要使用一些工具檢視字體,所以這邊我們下載一個叫 FontForge 的多功能字型編輯軟件,下載好後打開並選擇剛下載的 setofont.ttf,會看到這些很生動的手寫字體 :3

然後在選單中找到 View > Goto,因為我們知道「鄉」是其中一個缺字,所以就直接搜尋「鄉」
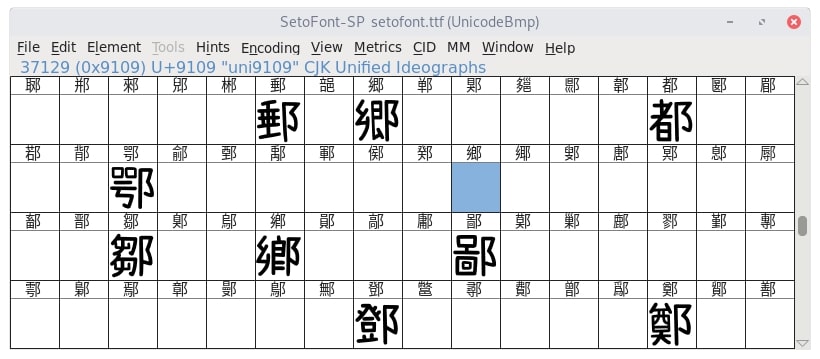
搜尋後發現「鄉」在這個字體中真的是空白一片,以我的理解是因為這字體把「鄉」字用空白填滿了,所以就算在我們眼中它是一個缺字,但系統也不這樣認為,至少 CSS 是這樣,所以接下來我們嘗試把「鄉」從字型中刪掉,在下面的空格地方右鍵然後選擇 Clear
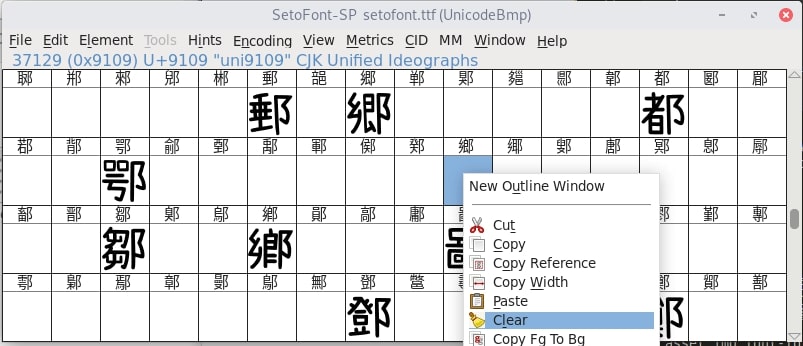

刪除後我們發現空格變成一個叉包了,之後在選單中選擇 File > Generate Fonts 儲存字型後我們再測試一次字體,這次「鄉」字有成功補上

移除所有空白字
為了讓系統把字補上,我的解決方法是把所有空白的字都刪除掉,所以我就寫了一個簡單的 Node.js 腳本
事前準備
我們需要以下工具
- Python 3
- Pip
- fonttools
- 示範用的瀨戶字體 Seto font
- Node.js
- 8GB 記憶體
安裝 pip 和 fonttools
先安裝 python 然後用以下指令安裝 pip
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py -o get-pip.py
python get-pip.py接著安裝 fonttools
pip install fonttools用 fonttools 把 .ttf 變成 xml
如果你還沒有下載瀨戶字體 Seto font,先下載好然後再用 fonttools 指令取得 setofont.ttx,.ttx 是 fonttools 的格式,實際上就是一個 xml 檔,其他字型檔論理上也可以用 fonttools 拆解成 xml,我們將會取得一個接近 100MB 的 .ttx 檔…
ttx ./setofont.ttf使用 Node.js 腳本把空白的字刪除
由於檔案太大,在沒有做 optimize 的情況下我們需要 8GB 的記憶體才能夠運行,在同一目錄下建立 index.js 檔案,複製下面的原碼然後執行以下指令
npm init -y
npm i node-expat xmlbuilder
node --max-old-space-size=8192 index.js這是 index.js
const fs = require("fs");
const expat = require("node-expat");
const builder = require("xmlbuilder");
// Change the source and dest file here
const src = fs.readFileSync("./setofont.ttx");
const destFileName = "out.ttx";
// Entry point
(async () => {
const filterList = await scan();
console.log(`Char to filter: ${filterList.length}`);
const xml = await parseXml(filterList);
})();
function scan() {
return new Promise((rs, rj) => {
let firstEle;
const filterList = [];
const parser = new expat.Parser("UTF-8");
parser.on("startElement", function (name, attrs) {
if (!firstEle) {
firstEle = name;
}
if (name === "TTGlyph" && attrs.yMin === undefined) {
filterList.push(attrs.name);
}
});
parser.on("endElement", function (name) {
if (firstEle === name) {
rs(filterList);
}
});
parser.on("error", function (error) {
console.error(error);
return rj(error);
});
parser.write(src);
});
}
function parseXml(filterList) {
return new Promise((rs, rj) => {
const parser = new expat.Parser("UTF-8");
let firstEle;
let root;
let levels = [];
let skip = false;
let skipEleName;
parser.on("startElement", function (name, attrs) {
if (!root) {
firstEle = name;
root = builder.create(name);
Object.keys(attrs).forEach((key) => {
root.att(key, attrs[key]);
});
levels.push(root);
} else if (!skip) {
// Skip
if (
filterList.includes(attrs.name) ||
filterList.includes(attrs.glyph) ||
filterList.includes(attrs.in)
) {
skip = true;
skipEleName = name;
} else {
const ele = levels[levels.length - 1].ele(name, attrs);
levels.push(ele);
}
}
});
parser.on("endElement", function (name) {
if (firstEle === name) {
// End
const xml = root.end({ pretty: false });
fs.writeFileSync(destFileName, xml);
} else {
if (skip) {
if (skipEleName === name) {
skip = false;
}
} else {
levels.pop();
}
}
});
parser.on("text", function (text) {
if (!skip) {
levels[levels.length - 1].text(text);
}
});
parser.on("error", function (error) {
console.error(error);
});
parser.write(src);
});
}運行後如無意外會產生 out.ttx,大小會比原來的 .ttx 檔小,因為我們把沒用的 xml tag 刪掉了,接下來再次使用 fonttools 指令把 ttx 還原成 ttf 檔
ttx ./out.ttx最後我們就可以得到不會出現缺字變成空白的 out.ttf 了﹗